This post was originally published on VMware vSphere Blog and I am just re-posting it here for future reference...
With the vSphere 6.5 release, DCLI has picked up a ton of new functionalities! DCLI can now interact with the vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA), perform VM tasks, receive environmental vSphere information, managing vSphere Tags, and work with the Content Library. This is definitely a great tool to have in the toolbox for anyone accessing a vSphere environment.
Accessing DCLI
DCLI is able to be installed on a multitude of Windows and Linux systems as part of the vSphere Command-Line Interface (vCLI). DCLI is also automatically included within the vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) as well as being included as part of the installation process for vCenter Server on Windows.Using DCLI
There are two ways to use DCLI, either in an interactive shell or via scripting mode. Both methods have their benefits, so it comes down to either preference or what fits the use case at the time.Interactive Shell
DCLI’s interactive shell has several great features, such as tab complete and session history retention and the ability to find a namespace just by starting it off with the first few characters.Accessing DCLI’s Interactive Shell
Here’s an example workflow of using DCLI’s interactive shell:- Start DCLI with the following options (Note: options start with a + in DCLI)
- +server -> The vCenter name/IP to connect to
- +skip-server-verification -> Instruct DCLI to ignore any certificate warnings
- +interactive -> Start the interactive mode
The example below shows a tab complete example when working with VM objects:
Scripting Mode
The scripting mode allows DCLI commands to be used within scripts. These scripts can then be turned into more extensive workflows and/or scheduled tasks.Calling DCLI commands through the scripting mode is fairly similar to interactive mode, but a server has to be specified each time. The full namespace has to be referenced as well.
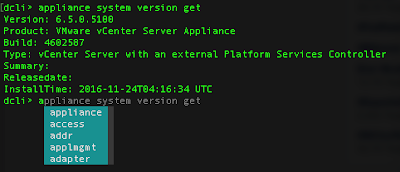
Here’s an example of retrieving the VCSA’s system version and then retrieving a list of VMs:
#!/bin/bash
COUNTER=0
while [ $COUNTER -lt 10 ]; do
echo Creating LoopVM$COUNTER
dcli com vmware vcenter vm create --name LoopVM$COUNTER --guest "SLES_12_64" --resource-pool "resgroup-9" --folder "group-v7" --datastore "datastore-12"
let COUNTER=COUNTER+1
done
bold=$(tput bold)
normal=$(tput sgr0)
echo ${bold}--- VM List ---${normal}
dcli com vmware vcenter vm list
Output Formatting
DCLI also has the ability to change how the output from commands are handled. The formatter allows users to specify outputs of CSV, HTML, JSON, Simple, Table, or XML.Here’s an example of using the formatter by showing a list of the hosts and then specifying the “+formatter json” parameter to receive the same output in JSON:
Credential Store
The first time a user connects to a vCenter server, they will be prompted to store the credentials to the credstore. After that initial save, the credstore will be referenced with each connection to that server. If needed, credentials can be specified at the command line to over-ride the values stored in the credstore.
Users can also work with the credstore to either populate credentials with the “+credstore-add +username user” parameter, remove credentials with the “+credstore-remove +user user +server servername.fqdn”, and list what credentials already exist with the “+credstore-list” parameter.
Here’s an example output from using the “+credstore-list” parameter within an interactive mode session:

Demonstration
Here’s a demonstration video showing DCLI’s interactive mode in action! The video details connecting to a VCSA, entering DCLI’s interactive mode, displaying some general environmental information as well as pointing out some of the benefits when using interactive mode, and lastly it creates a VM and shows all the important information about that new VM.Pay close attention to that VM creation command, there’s a sneak peak of an upcoming post in this series on DCLI.
Conclusion
DCLI has, relatively, flown under the radar up until this point. Interactive mode allows even brand new users to easily access and run commands within moments of connecting and without knowin the name of the name spaces or reading documentation. Scripting mode lets users have those same great commands available outside of the interactive shell and utilize them in a standalone basis or within a scheduled task or cron job. These commands can easily be used with the formatter option to produce a variety of outputs and allow quick integration into other products.For more information on getting started with DCLI, see the DCLI Reference.